Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Sound speeds#
Compute the “equilibrium” and “frozen” sound speeds for a gas
Requires: cantera >= 3.0.0, matplotlib
import cantera as ct
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def equilSoundSpeeds(gas, rtol=1.0e-8, max_iter=5000):
"""
Returns a tuple containing the equilibrium and frozen sound speeds for a
gas with an equilibrium composition. The gas is first set to an
equilibrium state at the temperature and pressure of the gas, since
otherwise the equilibrium sound speed is not defined.
"""
# set the gas to equilibrium at its current T and P
gas.equilibrate('TP', rtol=rtol, max_iter=max_iter)
# save properties
s0 = gas.s
p0 = gas.P
r0 = gas.density
# perturb the pressure
p1 = p0*1.0001
# set the gas to a state with the same entropy and composition but
# the perturbed pressure
gas.SP = s0, p1
# frozen sound speed
afrozen = math.sqrt((p1 - p0)/(gas.density - r0))
# now equilibrate the gas holding S and P constant
gas.equilibrate('SP', rtol=rtol, max_iter=max_iter)
# equilibrium sound speed
aequil = math.sqrt((p1 - p0)/(gas.density - r0))
# check against the built-in sound speed function
afrozen2 = gas.sound_speed
return aequil, afrozen, afrozen2
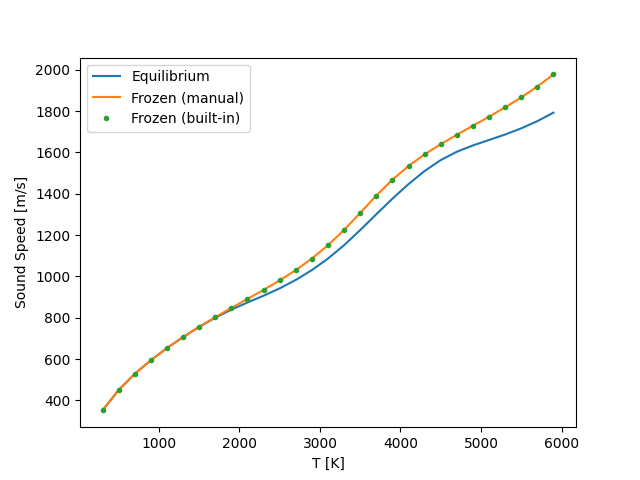
Calculate sound speed at a range of temperatures
gas = ct.Solution('gri30_highT.yaml')
gas.X = 'CH4:1.00, O2:2.0, N2:7.52'
T_range = np.arange(300, 5901, 200)
data = []
print(' T Equilibrium Frozen manual Frozen built-in')
print(' [K] [m/s] [m/s] [m/s]')
print('------- ----------- ------------- ---------------')
for T in T_range:
gas.TP = T, ct.one_atm
aequil, afrozen, afrozen2 = equilSoundSpeeds(gas)
data.append((T, aequil, afrozen, afrozen2))
print(f'{T:6.1f} {aequil:12.2f} {afrozen:13.2f} {afrozen2:15.2f}')
T Equilibrium Frozen manual Frozen built-in
[K] [m/s] [m/s] [m/s]
------- ----------- ------------- ---------------
300.0 351.82 351.82 351.83
500.0 450.54 450.54 450.54
700.0 528.57 528.57 528.58
900.0 594.39 594.39 594.39
1100.0 653.02 653.03 653.03
1300.0 706.54 706.64 706.64
1500.0 755.61 756.33 756.34
1700.0 800.09 803.03 803.04
1900.0 839.27 847.59 847.60
2100.0 873.72 891.07 891.07
2300.0 906.65 934.86 934.86
2500.0 942.15 980.70 980.70
2700.0 982.98 1030.52 1030.52
2900.0 1030.57 1086.41 1086.41
3100.0 1086.27 1150.69 1150.69
3300.0 1151.17 1224.86 1224.87
3500.0 1224.11 1307.11 1307.11
3700.0 1300.74 1390.78 1390.78
3900.0 1375.91 1467.77 1467.77
4100.0 1446.46 1533.98 1533.99
4300.0 1509.89 1590.28 1590.29
4500.0 1562.67 1639.67 1639.68
4700.0 1603.00 1685.06 1685.07
4900.0 1633.63 1728.73 1728.74
5100.0 1659.84 1772.45 1772.45
5300.0 1686.34 1817.70 1817.70
5500.0 1716.15 1865.92 1865.92
5700.0 1751.02 1918.55 1918.55
5900.0 1792.09 1977.10 1977.10
Plot results
data = np.array(data)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(data[:,0], data[:,1], label='Equilibrium')
ax.plot(data[:,0], data[:,2], label='Frozen (manual)')
ax.plot(data[:,0], data[:,3], linestyle='none', marker='.', label='Frozen (built-in)')
ax.set(xlabel='T [K]', ylabel='Sound Speed [m/s]')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.556 seconds)

