Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Interactive Reaction Path Diagrams#
This example uses ipywidgets to create interactive displays of reaction path
diagrams from Cantera simulations.
Requires: cantera >= 3.0.0, matplotlib >= 2.0, ipywidgets, graphviz, scipy
Tip
To try the interactive features, download the Jupyter notebook version of this
example: interactive_path_diagram.ipynb.
import numpy as np
from scipy import integrate
import graphviz
import os
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from collections import defaultdict
import cantera as ct
print(f"Using Cantera version: {ct.__version__}")
# Determine if we're running in a Jupyter Notebook. If so, we can enable the interactive
# diagrams. Otherwise, just draw output for a single set of inputs.
try:
from IPython import get_ipython
if "IPKernelApp" not in get_ipython().config:
raise ImportError("console")
if "VSCODE_PID" in os.environ:
raise ImportError("vscode")
except (ImportError, AttributeError):
is_interactive = False
else:
is_interactive = True
if is_interactive:
from IPython.display import display
from matplotlib_inline.backend_inline import set_matplotlib_formats
set_matplotlib_formats('pdf', 'svg')
from ipywidgets import widgets, interact
Using Cantera version: 3.1.0
When using Cantera, the first thing you usually need is an object representing some phase of matter. Here, we’ll create a gas mixture using GRI-Mech:
gas = ct.Solution("gri30.yaml")
Use Shock tube ignition delay measurement conditions corresponding to the experiments by Spadaccini and Colket [1].
CH₄-C₂H₆-O₂-Ar (3.29%-0.21%-7%-89.5%)
\(\phi\) = 1.045
P = 6.1 - 7.6 atm
T = 1356 - 1688 K
# Set temperature, pressure, and composition
gas.TPX = 1550.0, 6.5 * ct.one_atm, "CH4:3.29, C2H6:0.21, O2:7 , Ar:89.5"
Residence time is close to ignition delay reported by Spadaccini and Colket (1994).
residence_time = 1e-3
Create a batch reactor object and set solver tolerances
reactor = ct.IdealGasConstPressureReactor(gas, energy="on")
reactor_network = ct.ReactorNet([reactor])
reactor_network.atol = 1e-12
reactor_network.rtol = 1e-12
Store time, pressure, temperature and mole fractions
Interactive reaction path diagram#
When executed as a Jupyter Notebook, the plotted time step, threshold and element can be changed using the slider provided by IPyWidgets.
def plot_reaction_path_diagrams(plot_step, threshold, details, element):
P = profiles["pressure"][plot_step]
T = profiles["temperature"][plot_step]
X = profiles["mole_fractions"][plot_step]
time = profiles["time"][plot_step]
gas.TPX = T, P, X
diagram = ct.ReactionPathDiagram(gas, element)
diagram.threshold = threshold
diagram.title = f"time = {time:.2g} s"
diagram.show_details = details
graph = graphviz.Source(diagram.get_dot())
if is_interactive:
display(graph)
else:
return graph
if is_interactive:
interact(
plot_reaction_path_diagrams,
plot_step=widgets.IntSlider(value=100, min=0, max=steps-1, step=10),
threshold=widgets.FloatSlider(value=0.1, min=0.001, max=0.4, step=0.01),
details=widgets.ToggleButton(),
element=widgets.Dropdown(
options=gas.element_names,
value="C",
description="Element",
disabled=False,
),
)
else:
# For non-interactive use, just draw the diagram for a specified time step
diagram = plot_reaction_path_diagrams(
plot_step=100,
threshold=0.1,
details=False,
element="C"
)
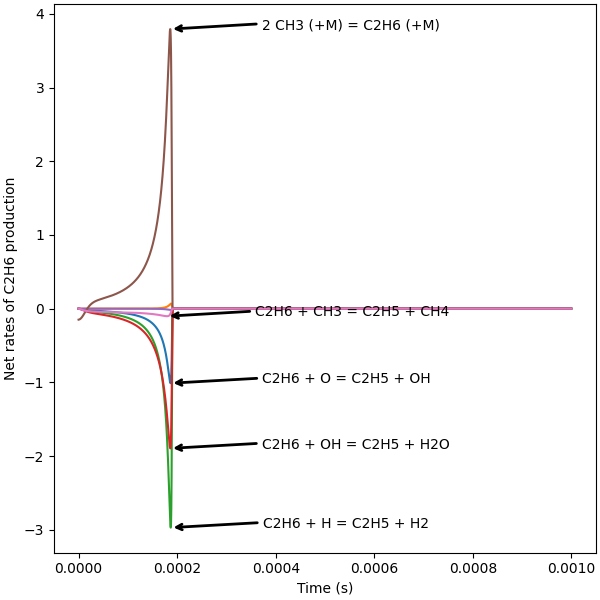
Interactive plot of instantaneous fluxes#
Find reactions containing the species of interest, C₂H₆ in this case.
C2H6_stoichiometry = np.zeros_like(gas.reactions())
for i, r in enumerate(gas.reactions()):
C2H6_moles = r.products.get("C2H6", 0) - r.reactants.get("C2H6", 0)
C2H6_stoichiometry[i] = C2H6_moles
C2H6_reaction_indices = C2H6_stoichiometry.nonzero()[0]
The following cell calculates net rates of progress of reactions containing the species of interest and stores them.
profiles["C2H6_production_rates"] = []
for i in range(len(profiles["time"])):
X = profiles["mole_fractions"][i]
t = profiles["time"][i]
T = profiles["temperature"][i]
P = profiles["pressure"][i]
gas.TPX = (T, P, X)
C2H6_production_rates = (
gas.net_rates_of_progress
* C2H6_stoichiometry # [kmol/m^3/s]
* gas.volume_mass # Specific volume [m^3/kg].
) # overall, mol/s/g (g total in reactor, same basis as N_atoms_in_fuel)
profiles["C2H6_production_rates"].append(
C2H6_production_rates[C2H6_reaction_indices]
)
# Create the instantaneous flux plot. When executed as a Jupyter Notebook, the threshold
# for annotating of reaction strings can be changed using the slider provided by
# IPyWidgets.
plt.rcParams["figure.constrained_layout.use"] = True
def plot_instantaneous_fluxes(profiles, annotation_cutoff):
profiles = profiles
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.plot(profiles["time"], np.array(profiles["C2H6_production_rates"]))
for i, C2H6_production_rate in enumerate(
np.array(profiles["C2H6_production_rates"]).T
):
peak_index = abs(C2H6_production_rate).argmax()
peak_time = profiles["time"][peak_index]
peak_C2H6_production = C2H6_production_rate[peak_index]
reaction_string = gas.reaction_equations(C2H6_reaction_indices)[i]
if abs(peak_C2H6_production) > annotation_cutoff:
plt.annotate(
reaction_string.replace("<=>", "="),
xy=(peak_time, peak_C2H6_production),
xytext=(
peak_time * 2,
(
peak_C2H6_production
+ 0.003
* (peak_C2H6_production / abs(peak_C2H6_production))
* (abs(peak_C2H6_production) > 0.005)
* (peak_C2H6_production < 0.06)
),
),
arrowprops=dict(
arrowstyle="->",
color="black",
relpos=(0, 0.6),
linewidth=2,
),
horizontalalignment="left",
)
plt.xlabel("Time (s)")
plt.ylabel("Net rates of C2H6 production")
plt.show()
if is_interactive:
interact(
plot_instantaneous_fluxes,
annotation_cutoff=widgets.FloatSlider(value=0.1, min=1e-2, max=4, steps=10),
profiles=widgets.fixed(profiles)
)
else:
plot_instantaneous_fluxes(annotation_cutoff=0.1, profiles=profiles)
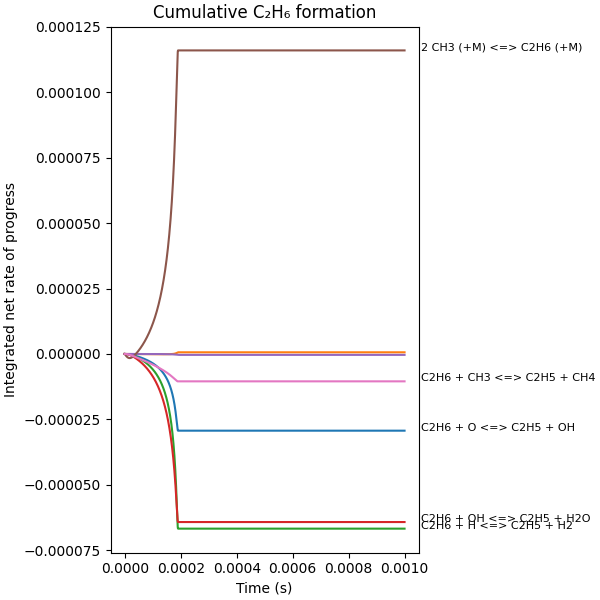
Interactive plot of integrated fluxes#
When executed as a Jupyter Notebook, the threshold for annotating of reaction strings can be changed using the slider provided by iPyWidgets
# Integrate fluxes over time
integrated_fluxes = integrate.cumulative_trapezoid(
np.array(profiles["C2H6_production_rates"]),
np.array(profiles["time"]),
axis=0,
initial=0,
)
def plot_integrated_fluxes(profiles, integrated_fluxes, annotation_cutoff):
profiles = profiles
integrated_fluxes = integrated_fluxes
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.plot(profiles["time"], integrated_fluxes)
final_time = profiles["time"][-1]
for i, C2H6_production in enumerate(integrated_fluxes.T):
total_C2H6_production = C2H6_production[-1]
reaction_string = gas.reaction_equations(C2H6_reaction_indices)[i]
if abs(total_C2H6_production) > annotation_cutoff:
plt.text(final_time * 1.06, total_C2H6_production, reaction_string,
fontsize=8)
plt.xlabel("Time (s)")
plt.ylabel("Integrated net rate of progress")
plt.title("Cumulative C₂H₆ formation")
plt.show()
if is_interactive:
interact(
plot_integrated_fluxes,
annotation_cutoff=widgets.FloatLogSlider(
value=1e-5, min=-5, max=-4, base=10, step=0.1
),
profiles=widgets.fixed(profiles),
integrated_fluxes=widgets.fixed(integrated_fluxes)
)
else:
plot_integrated_fluxes(
profiles=profiles,
integrated_fluxes=integrated_fluxes,
annotation_cutoff=1e-5
)
References#
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.775 seconds)

