Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Acceleration of reactor integration using a sparse preconditioned solver#
Ideal gas, constant-pressure, adiabatic kinetics simulation that compares preconditioned and non-preconditioned integration of n-hexane.
Requires: cantera >= 3.2.0, matplotlib >= 2.0
import cantera as ct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.constrained_layout.use'] = True
from timeit import default_timer
Simulation setup#
Create a reactor network for simulating the constant pressure ignition of a stoichiometric n-hexane/air mixture, with or without the use of the preconditioned solver.
def integrate_reactor(preconditioner=True):
# Use a detailed n-hexane mechanism with 1268 species
gas = ct.Solution('example_data/n-hexane-NUIG-2015.yaml')
gas.TP = 1000, ct.one_atm
gas.set_equivalence_ratio(1, 'NC6H14', 'N2:3.76, O2:1.0')
reactor = ct.IdealGasConstPressureMoleReactor(gas, clone=False)
# set volume for reactors
reactor.volume = 0.1
# Create reactor network
sim = ct.ReactorNet([reactor])
# Add preconditioner
if preconditioner:
sim.derivative_settings = {"skip-third-bodies":True, "skip-falloff":True}
sim.preconditioner = ct.AdaptivePreconditioner()
sim.initialize()
# Advance to steady state
integ_time = default_timer()
# solution array for state data
states = ct.SolutionArray(reactor.phase, extra=['time'])
# advance to steady state manually
while (sim.time < 0.1):
states.append(reactor.phase.state, time=sim.time)
sim.step()
integ_time = default_timer() - integ_time
# Return time to integrate
if preconditioner:
print(f"Preconditioned Integration Time: {integ_time:f}")
else:
print(f"Non-preconditioned Integration Time: {integ_time:f}")
# Get and output solver stats
for key, value in sim.solver_stats.items():
print(f"{key:>24s}: {value}")
print("\n")
# return some variables for plotting
return states.time, states.T, states('CO2').Y, states('NC6H14').Y
Integrate with sparse, preconditioned solver#
Preconditioned Integration Time: 2.223525
step_solve_fails: 10
steps: 981
rhs_evals: 1187
nonlinear_iters: 1184
nonlinear_conv_fails: 28
err_test_fails: 29
last_order: 2
stab_order_reductions: 0
jac_evals: 0
lin_solve_setups: 137
lin_rhs_evals: 3788
lin_iters: 3788
lin_conv_fails: 263
prec_evals: 39
prec_solves: 4882
jt_vec_setup_evals: 0
jt_vec_prod_evals: 3788
Integrate with direct linear solver#
Non-preconditioned Integration Time: 21.184521
step_solve_fails: 0
steps: 2704
rhs_evals: 4294
nonlinear_iters: 4291
nonlinear_conv_fails: 36
err_test_fails: 160
last_order: 5
stab_order_reductions: 0
jac_evals: 61
lin_solve_setups: 378
lin_rhs_evals: 77409
lin_iters: 0
lin_conv_fails: 0
prec_evals: 0
prec_solves: 0
jt_vec_setup_evals: 0
jt_vec_prod_evals: 0
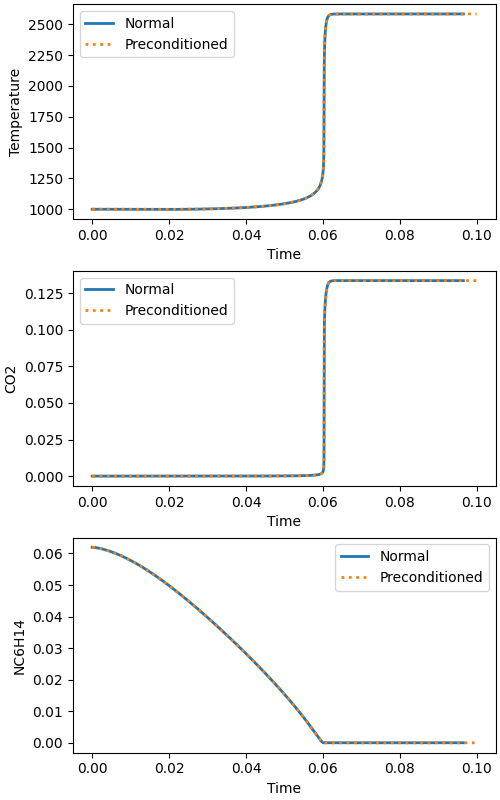
Plot selected state variables#
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(5, 8))
# temperature plot
ax1.set_xlabel("Time")
ax1.set_ylabel("Temperature")
ax1.plot(timenp, Tnp, linewidth=2)
ax1.plot(timep, Tp, linewidth=2, linestyle=":")
ax1.legend(["Normal", "Preconditioned"])
# CO2 plot
ax2.set_xlabel("Time")
ax2.set_ylabel("CO2")
ax2.plot(timenp, CO2np, linewidth=2)
ax2.plot(timep, CO2p, linewidth=2, linestyle=":")
ax2.legend(["Normal", "Preconditioned"])
# C12H26 plot
ax3.set_xlabel("Time")
ax3.set_ylabel("NC6H14")
ax3.plot(timenp, NC6H14np, linewidth=2)
ax3.plot(timep, NC6H14p, linewidth=2, linestyle=":")
ax3.legend(["Normal", "Preconditioned"])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 24.237 seconds)

